Smoking, Vaping and the Skin.
Smoking, Vaping, and the Skin: What Happens to Your Skin When You Smoke or Vape?
Smoking has been a well-known cause of health problems for decades, but the impact of smoking on the skin often receives less attention. With the rise of e-cigarettes (e-cigarettes or vaping), it is more important than ever to understand how both traditional and modern smoking habits can affect your skin. Smoking and vaping can have harmful effects on the skin, such as premature aging, delayed wound healing, and an increased risk of skin conditions. To better understand this, we’ve delved into the scientific literature.
The Effects of Smoking on the Skin
Smoking damages the skin at several levels. Cigarette smoke breaks down collagen and elastin, the proteins responsible for the skin’s firmness and elasticity. This leads to premature aging and the formation of wrinkles. Free radicals, which are produced by the burning of tobacco, cause oxidative stress, meaning they damage healthy skin cells and reduce their ability to repair themselves. As a result, the skin becomes more vulnerable, thinner, and shows signs of aging like wrinkles, sagging, and a dull complexion.
Vaping: A "Safer" Alternative?
E-cigarettes, often promoted as a safer alternative to traditional cigarettes, have been shown by research to have similar harmful effects on the skin. Vaping can also lead to skin problems. Although e-cigarettes do not cause the burning of tobacco like regular cigarettes, they contain other harmful chemicals that can damage the skin. For instance, the nicotine content in vaping disrupts blood flow to the skin, which can lead to dry, dull, and aged skin, much like traditional smoking.
Worse Wound Healing from Smoking and Vaping
Both cigarettes and e-cigarettes negatively affect wound healing. Smoking reduces collagen production and slows down the migration of fibroblasts, the cells important for skin repair. This leads to slower wound healing, an increased risk of infections, and even tissue necrosis (skin tissue death) after surgeries. Additionally, smokers may develop more scars due to poor wound healing.
Allergies and Skin Irritations from Smoking and Vaping
Another lesser-known consequence of smoking is the development of contact allergies. Cigarette smoke contains allergens like formaldehyde, menthol, and even cocoa, which can cause allergic reactions such as hand dermatitis. This type of skin inflammation is especially common in smokers who touch cigarettes with their hands. E-cigarettes can also cause contact allergies, particularly from metals like nickel, which are often used in the devices. For example, a case was described where a patient with a nickel allergy developed a rash from touching their e-cigarette.
Dermatological Conditions from Smoking and Vaping
In addition to skin aging and poor wound healing, smoking can contribute to the development of skin conditions such as psoriasis, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP). The risk of SCC, a form of skin cancer, increases among smokers. The prevalence of such skin conditions among smokers highlights the significant impact of tobacco use on overall skin health. This also applies to vapers, who can experience inflammation and rashes due to the chemicals in e-liquids.
Stoptober
Every year in October, the month is dedicated to Stoptober, a campaign that encourages smokers to quit for 28 days. What began in 2012 in the United Kingdom, initiated by Public Health England, has since become an annual event in several countries, including the Netherlands. Since 2014, the Netherlands has enthusiastically joined this challenge. The idea behind Stoptober is simple but effective: if you manage to stay smoke-free for 28 days, you have a much greater chance of quitting permanently.
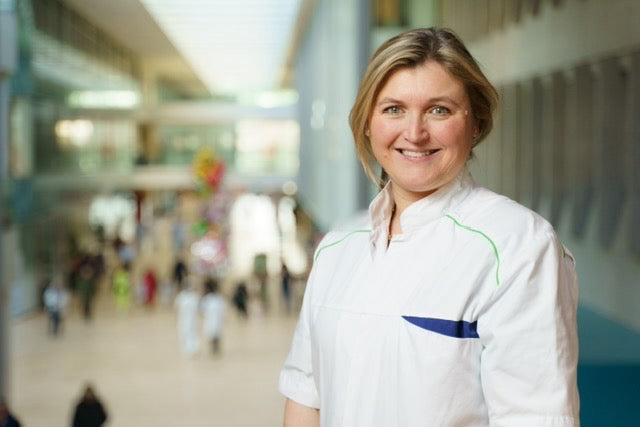
Dr. Annemarie de Lind van Wijngaarden, a pulmonologist at the HAGA hospital in The Hague, emphasizes that it’s never too late to quit smoking. "Every cigarette you don’t smoke is a win," she says. Quitting smoking has an immediate positive effect on your energy, endurance, appearance, and sleep quality. After 12 weeks, the risk of a heart attack decreases, and your lung function improves. One year after quitting, the risk of heart disease is halved, and 10 years later, the increased risk of lung cancer is also halved.
Additionally, it is crucial to work together towards a Smoke-Free Generation, says De Lind van Wijngaarden. "We all have a responsibility to ensure that young people and children don’t start smoking because addiction is difficult to overcome." By quitting, you set a good example and protect children from the harmful effects of tobacco.
Conclusion
It is clear that both cigarettes and e-cigarettes have harmful effects on the skin. They cause premature aging, slow down wound healing, and increase the risk of skin conditions. Although e-cigarettes are often seen as a safer alternative to traditional cigarettes, research shows that vaping also has negative consequences for skin health. The best thing you can do for your skin – and your overall health – is to quit smoking and vaping.
Sources:
1 Ortiz, A., & Grando, S. A. (2012). Smoking and the skin. International Journal of Dermatology, 51(2), 250-262. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05205.x
2 Mitri, A., Lin, G., Waldman, R. A., & Grant-Kels, J. M. (2021). Effects of tobacco and vaping on the skin. Clinics in Dermatology, 39(5), 785-792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.05.004
Special thanks to Annemarie de Lind van Wijngaarden, pulmonologist
Share